World Web Accessibility Awareness Day is celebrated every year to raise visibility on the importance of digital accessibility. In an increasingly virtual world, it is crucial to ensure that all individuals, regardless of their abilities or disabilities, can access and use the information, services, and products available online.
We all have the right to access online newspapers and news, make purchases or banking transactions, play video games, take a course, or engage in any other online activity. Currently, we are experiencing a significant digital transformation. Video conferences, remote work, social media, distance education, telemedicine, basic public services for citizens, and cultural and multimedia content, among others, are just a few important examples that demonstrate why we need to promote digital accessibility.
How Do We Ensure Digital Accessibility?
Currently, there are many regional and national regulations that promote and guarantee digital accessibility in Latin America and the Caribbean. There are also guidelines, examples, and methods to achieve this goal. Some examples of effective practices include:
- Making changes to the design and structure of websites or mobile applications to facilitate their use.
- Providing alternative content for those who cannot see or hear online content.
- Allowing voice control, remote control, and keyboard input.
- Providing clear and easy-to-follow navigation.

Four Principles of Digital Accessibility
In general, the key is to ensure digital accessibility and universal access to products and services through four basic principles:
1. Perceivable:
Content should be perceivable by all individuals, regardless of their sensory abilities. This means that the content should be easily visible, audible, and understandable for all users.
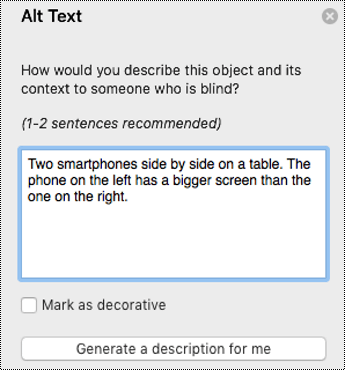
An example is the use of captions in videos and audio transcriptions to make auditory content accessible to people with hearing disabilities. Additionally, visual content such as images can have alternative text descriptions (alt text) so that people with visual impairments can access them. Another simple example is not relying solely on colors to convey information since a percentage of the population is color-blind. Signage or information, such as traffic lights, should not be limited to colors alone, allowing more people to understand them.
2. Operable:
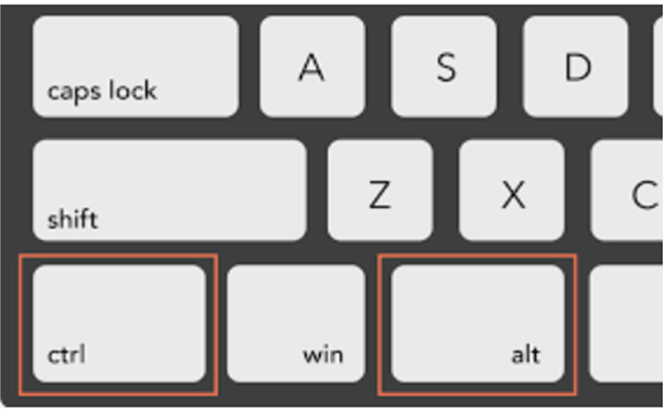

Content should be operable by all individuals, regardless of their physical or cognitive abilities. This means that users should be able to navigate and use the content effectively, regardless of the technology or devices they use, such as keyboards, touch screens, and voice input, among others.
A concrete example is the use of keyboard shortcuts on a website to allow users to navigate the page without using a mouse, which is useful for people with motor disabilities. A pause button can also be added to a slideshow presentation to allow users to stop and review the content at their own pace.
3. Understandable:
Content should be understandable by all individuals, regardless of their cognitive or linguistic abilities. This means that the content of digital products should be easy to understand and use, with clear language and the use of simple wording and terminology. It ensures that it is easy to comprehend for all individuals, including those with cognitive disabilities.
4. Robust:
Content should be robust and compatible with a variety of technologies and devices to ensure that all individuals can access the content without issues. An example is the use of web standards and clean coding practices, which ensure that the website functions properly on different platforms, browsers, and devices.
Accessibility is a Right
In conclusion, digital accessibility is essential to guarantee inclusion and ensure that all citizens have access to online services and products. By promoting accessibility, not only will the reach and participation of each website or online platform increase, but it will also comply with local and international laws and regulations, improve the user experience, save costs, and achieve greater positioning.
Therefore, digital accessibility is important not only for people with disabilities, for whom it is indispensable, but also as a right that benefits all citizens and promotes inclusion and access to services and products for everyone.

Leave a Reply