Grenada: Energy Market Overview
The island state of Grenada is located at the southern end of the Grenadines in the eastern Caribbean. The state’s territory encompasses the three major islands Grenada, Carriacou and Petite Martinique, as well as a number of smaller islands. Together the islands are home to a population of 110,000 people. More than 90 percent of the population live on Grenada and about one third reside in the national capital of St. George’s. The national economy is dominated by service sector, primarily government services, education, banking and insurance, tourism and communications, which contributes 78 percent to the GDP. Industry and agriculture contribute 16 percent and 6 percent respectively. (IRENA, 2012) The tourism sector directly contributes to 7.3 percent of GDP but taking multiplier effects into account the sectors contribution is estimated to be around 24 percent. (Organization of American States, 2010)
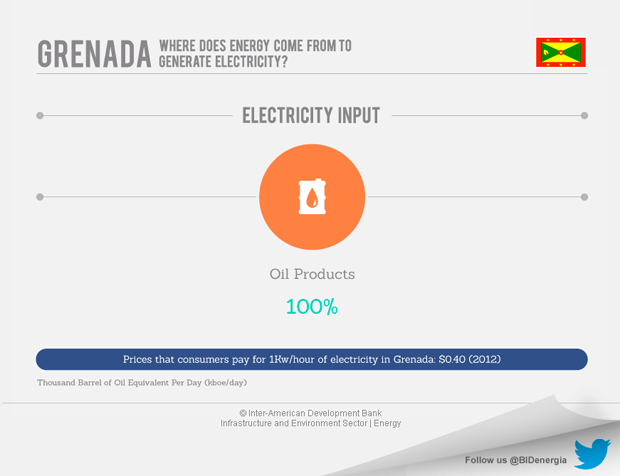
Grenada is almost wholly dependent on imported oil products which provide 93 percent of its overall energy supply. The remaining 7 percent are provided by combustible renewables & waste.
Grenada Electricity Services Ltd. (GRENLEC), a private-public owned utility company, holds a monopoly on the generation, transmission and distribution of electricity, and provides electricity to the islands of Grenada, Petite Martinique, and Carriacou. Virtually all of Grenada’s electricity is generated with diesel. (Government of Grenada, 2011) GRENLEC operates diesel power plants at Queens Park on the main island of Grenada with an installed capacity of 45.9 MW. In addition it has capacity of 3.2 MW on Carriacou, 0.5 MW on Petit Martinique, and 2.8 MW of backup capacity on the campus of St. George’s University. (Castalia Consulting, 2012; Government of Grenada, 2011; Organization of American States, 2010; World Bank, 2010)
GRENLEC sold a total of 185.8 GWh to 41,222 customers. The cost of oil imports used for the generation of electricity is substantial representing 7 percent of total imports by value and equaling 76 percent of export revenues. Electricity prices, as in many other small islands states in the Caribbean, rank among the highest in the world and reached 0.64 US$ per kWh in 2008. (Government of Grenada, 2011; Grenada Electricity Services Ltd., 2012)
About half of Grenada’s energy supply is consumed by the transportation sector followed by the electricity sector at 40 percent. (IRENA, 2012) Electricity consumption in Grenada is dominated by the commercial sector, which accounts for 57 percent of consumed electricity, followed by the residential sector at 38%. Industrial consumption stands at 3 percent and street lighting at 2 percent. Between 2000 and 2008 GRENLEC reduced system losses from 13 percent of generation to 9 percent. (Government of Grenada, 2011; Organization of American States, 2010)
Grenada: Energy and Electricity Sector Regulatory Framework

The Ministry of Finance, Planning, Economy, Energy & Cooperatives holds a broad mandate with responsibility for the energy sector. Within the ministry, the Department of Energy & Sustainable Development is tasked to ensure adequate, reliable and economical energy services and satisfy projected future demand. It is also responsible to encourage the use and promotion of renewable energy. (Organization of American States, 2010; Renewable Energy & Energy Efficiency Partnership, 2012)
The Electricity Supply Ordinance of 1961 provides GRENLEC with exclusive license for the generation, transmission, distribution and sale of electricity for a period of 80 years. (Grenada Electricity Services Ltd., 2012)In 1982 the Grenada government became the sole owner of GRENLECO which lasted until 1994 when the it sold all but a 10 percent stake to investors. A new Electricity Supply Act of the same year reaffirmed GRENLEC’s market dominating position and granted it a monopoly until December 31, 2073. (Castalia Consulting, 2012; Grenada Electricity Services Ltd., 2012; Renewable Energy & Energy Efficiency Partnership, 2012; World Bank, 2010)
Recently GRENLEC agreed to purchase electricity produced by GRENSOL up to a limit of 1 percent of total demand. As GRENSOL is likely to expand its efforts it is likely that the arbitrary 1 percent limit, set by GRENLAC, will be exceeded in the near future and may be “subject to review and negotiations” as part of a revised Electricity Supply Act. (Government of Grenada, 2011)
Castalia Consulting. (2012). Sustainable Energy in the Eastern Caribbean : Achieving an Unrealized Potential Report to the.
Government of Grenada. (2011). A Low Carbon Development Strategy for Grenada, Carriacou and Petite Martinique.
Grenada Electricity Services Ltd. (2012). GRENLEC Annual Report 2012. Retrieved from http://www.grenlec.com/images/Annual_Reports/Report2012.pdf
IRENA. (2012). Grenada Renewables readiness assessment.
Organization of American States. (2010). Energy Policy and Sector Analysis in the Caribbean 2010-2011.
Renewable Energy & Energy Efficiency Partnership. (2012). Grenada. Retrieved from http://www.reegle.info/policy-and-regulatory-overviews/GD
World Bank. (2010). Caribbean Regional Electricity Generation , Interconnection, and Fuels Supply Strategy Final Report.
Leave a Reply