Este artículo está también disponible en / This post is also available in: Spanish
Cities in Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC) play a key role in providing services to their inhabitants. They are the administrative level closest to the needs of citizens, offering crucial services such as electricity, water, transportation, waste management and public infrastructure. In some countries in the region, they also manage education, health and security.
In order to provide all municipal services, cities need access to sources of financing. As we discussed in the first article of this series about subnational financing, municipalities obtain it in many ways. The most traditional are local, regional, or national sources (such as taxes, fees, or transfers). They can also access loans or grants, and obtain benefits through land readjustments and joint ventures, or public-private partnerships, as in the cases of Washington DC and Bilbao. There is also another increasingly common instrument: municipal funds.
What are municipal funds and how do they work? In today’s article, we will answer these questions, at the IDB we believe they can be a key tool for financing sustainable development in our region.
What are municipal development funds?
Municipal development funds are nationally established financial intermediaries that channel resources in the form of loans or grants and, in some cases, blended financing. They can take the form of banks, trusts and other entities. These funds have been widely used in OECD countries and other emerging economies. They have proven to be instrumental in promoting fiscal discipline and building capacity for project development, repayment and credit history in local governments.
The role of municipalities in sustainable development
Before delving into the details of municipal funds, it is essential to highlight the role of local governments in public investment and sustainable development. This importance is reflected in several documents, such as the UN Secretary General’s Synthesis Report on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which notes that “most of the investments to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals will take place at the subnational level and will be led by local authorities.” In the same vein, a High Level Panel, in relation to the Post-2015 agenda, argues that the fight for sustainable development will be decided in cities. Similarly, the Addis Ababa Action Agenda on Financing for Development emphasizes the subnational role in financing for development and commits to increasing international cooperation to support subnational governments in achieving this purpose.

There are at least three factors that explain the importance of local governments in sustainable development:
- Deficits in infrastructure and services: many countries in the region face deficits in infrastructure and services. To cover these deficits, planning and investment are required, in which subnational governments can play a key role, as international evidence indicates.
- Population growth and urbanization: Population growth and urbanization increase the demand for infrastructure. Despite their importance in economic growth, urban areas face challenges in employment generation and the provision of public services. There is a need to improve public investments and promote an enabling environment for private investments at the local level.
- Subnational governments and the SDGs: Subnational governments are essential to address the SDGs and global development goals in an integrated manner, especially in the area of sustainable cities. These governments are closer to citizens and can drive integrated territorial development. 61% of SDG targets require attention at the local level.
How do municipal funds work?
Municipal funds seek to close gaps in access to financial resources to support territorial investments that contribute to sustainable development. They can provide grants and financing through various mechanisms and programs aimed at supporting local or regional development projects and activities. These resources are usually earmarked for priority areas such as urban infrastructure, transportation and mobility, climate change adaptation and local economic development, among others. The following are some of the ways in which municipal funds mobilize their resources:
- Grants: municipal funds can allocate resources directly to subnational governments through grants for those entities that do not have the capacity for debt repayment or to support the development of investment projects that are not bankable.
- Loans: municipal funds may also allocate resources to finance public investment projects or in collaboration with the private sector. Access to these funds is generally reserved for subnational entities that have the capacity to repay debt or for projects that can generate positive cash flow and are, in effect, bankable.
- Blended finance: Municipal funds can also provide blended finance. That is, they mobilize both public and private resources to finance investment projects. This approach maximizes the impact of available resources, diversifies the sources of financing and reduces the risks associated with the investment.
How are municipal funds implemented?
Generally, municipal funds establish eligibility criteria to ensure that selected projects align with national development priorities and local needs. Below are some common eligibility criteria for funding:
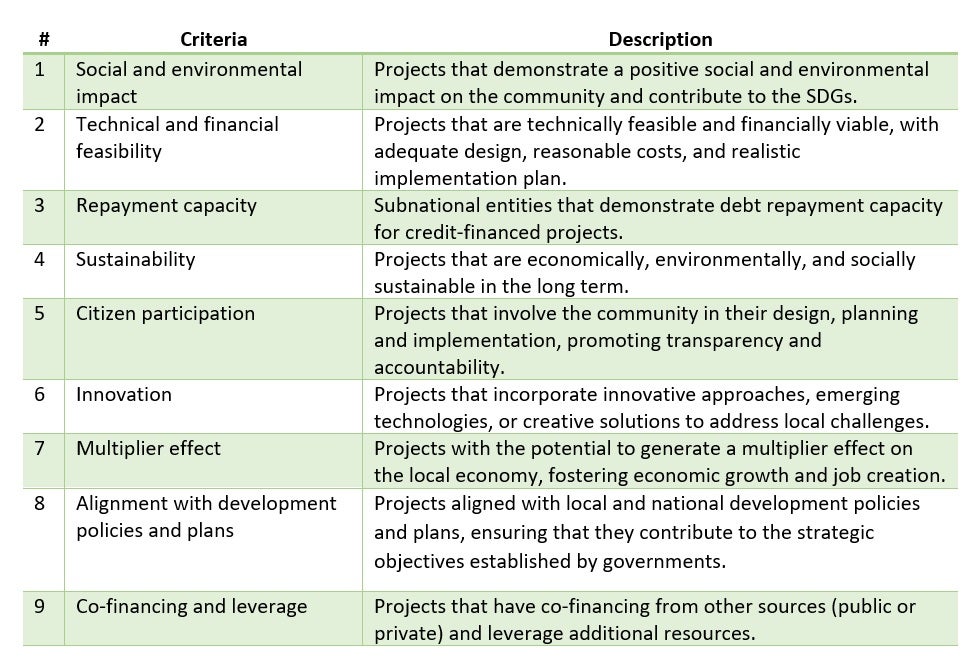
The execution of municipal funds may vary depending on the country and the established governance structure. Generally, municipalities are responsible for the implementation and execution of projects financed by municipal funds. However, there may also be cases where the national government or intermediate entities play a role in overseeing and supporting project implementation. The following are some of the ways in which the funds can be executed:
- Direct execution by municipalities: municipalities are responsible for the planning, management and execution of projects financed by municipal funds. This involves contracting suppliers, procuring materials, supervising construction and ensuring compliance with established deadlines and budgets.
- Execution through trusts: In some countries, municipal funds are administered and executed through trusts. In this model, the municipal fund is established as an independent trust, with a board of directors in charge of the management and execution of the financed projects.
- Implementation with support from the national government: in some cases, the national government may provide technical, financial and administrative assistance to the municipalities in the implementation of the projects.
How can municipal funds contribute to the region’s development?
In the next article we will explain how this type of financing can play a crucial role in the development of LAC. Until then, we invite you to share your opinion in the comments section – we look forward to hearing from you!
Related content:







How it´s possible to know the rules or conditions of this kind of funds you have available in order to help Municipalities to prepare or design well done projects that could receive those funds