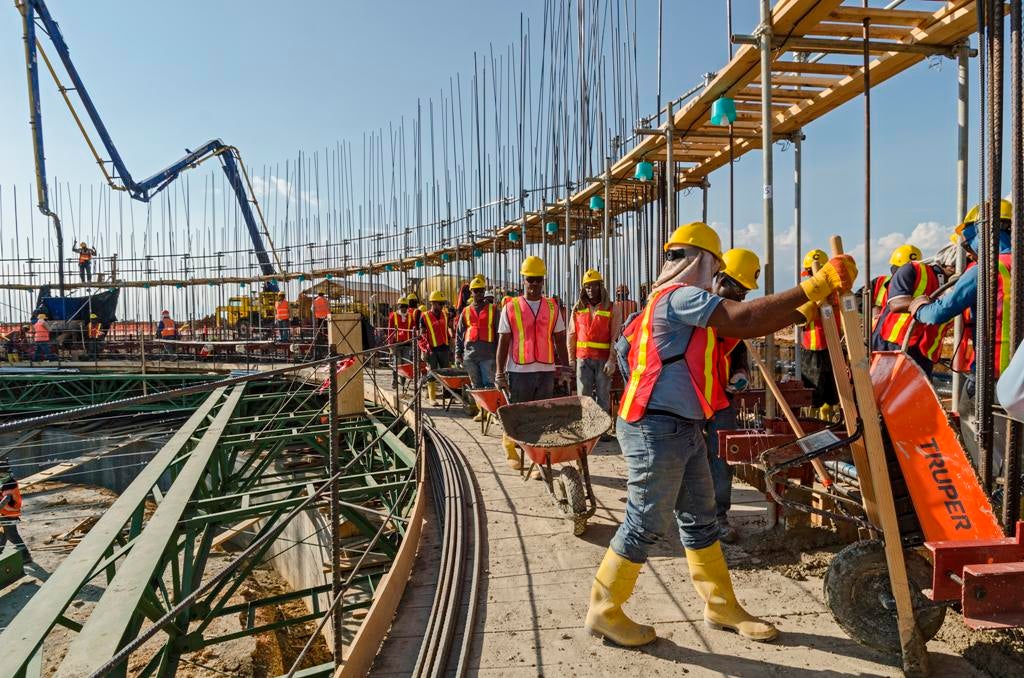
My professional experience in Occupational Safety and Health has shown me that companies that implement and effectively maintain Occupational Safety and Health Management Systems (OSHMS) get a number of benefits that make them more competitive. This is because OSHMS:
- Improve the ratings used to gain access to bids and to projects with potential clients.
- Reduce the number of accidents and therefore also the amount of downtime and its associated costs.
- Boost corporate profile, helping attract and retain better-trained personnel.
- Improve institutional credibility, as certification provides assurances to interested parties.
- Strengthen Occupational Safety and Health (OS&H) at all levels of the organization.
- Provide increased access to new clients and business partners.
- Dramatically reduce OS&H-related costs and insurance premiums.
- Simplify compliance with applicable legislation.
However, implementation of this system demands hard work and requires cooperation from all sectors of an organization. Quite often implementation faces hurdles due to lack of support at managerial level and of a culture of prevention among the organization’s staff.
OSHMS’s success, or lack thereof, depends on the organization’s culture. In other words, preventive management results are determined not just by components (procedures, policies, protocols, instructions, etc.) but also by the cultural context that is at play. Therefore, Occupational Safety and Health management must first focus on generating that preventive culture. This cannot be achieved by the imposition of conditions. Rather, it must be built from the bottom up after gaining the personal engagement of each member of the organization and combining it with leadership, supervisors’ commitment, workers participation, and upper management support.
Upper management, together with the company’s middle and supervisor levels, are key to the implementation of the system, whose principles and actions play a crucial role in defining the organization’s OS&H culture. The companies that have this culture in place also have, as a common denominator, the personal involvement of upper management, whose commitment to the wellbeing of employees is in itself a factor that encourages workers to do a good job.
The Inter-American Development Bank’s Safeguards Policy OP-703, through its directives (B.2 Country Laws and Regulations; B.4 Other Risk Factors; B.5 Environmental Assessment Requirements; B.10 Hazardous Materials; and B.17 Procurement) require that projects financed by the IDB implement Occupational Safety and Health plans and programs to guarantee compliance with OS&H risk control standards in their activities. Additionally, with the implementation of directive B.7 (Supervision and Compliance) by way of visits, inspections, and/or audits, safeguards specialists make sure that all projects are executed in compliance with OS&H standards and OP-703 Policies.
Central and South American countries have in place national legislation governing corporate compliance with Occupational Safety and Health programs. Let me now share the names of some of the institutions that have developed international standards to create safe working conditions that help determine the appropriate risk control steps in the different activities of your company and of projects financed by the Bank:
OSHA: Occupational Safety and Health Administration
- General Industries: 29 CFR 1910
- Construction Industry: 29 CFR 1926
- Maritime Industry: 29 CFR 1915
- Marine Terminal Operation: 29 CFR 1917
- Agriculture: 29 CFR 1928…
ANSI: The American National Standards Institute
NFPA: National Fire Protection Association
NIOSH: National Institute Occupational Safety and Health
IFC: International Finance Corporation
*OHSAS 18001: Occupational Safety and Health Management Systems (OSHMS) – Requirements
*When discussing Occupational Safety and Health Management Systems (OSHMS), reference must be made to the OHSAS 18001 standard. Although it is now in the process of being included in the ISO standards series –specifically in ISO 445001–, it is currently in force; OHSAS 18001 is a demonstrable and voluntary standard that sets outs the requirements for an effective OSHMS establishment and operation.

Leave a Reply