*By: Paula Guerra
Can you picture yourself reporting the amount and type of waste found in public spaces, so that cleanup efforts can be undertaken with citizen participation through a mobile application? This concept, which may seem futuristic, already exists in cities where digital technology revolutionized the way we see and manage solid waste. Yet, this innovation is not far-reaching enough. This is why the IDB Group and its partners created Source of Innovation, an alliance that fosters the development and implementation of digital and social innovation in the solid waste sector and promotes efficient, safe and timely access to public services throughout the region.
Industry 4.0 or smart technology has positively impacted solid waste management systems through the development of tools that tackle the main challenges of waste management, such as cleaning, collecting, transporting, recovery/recycling and final disposal. Digital technologies with greater exposure in the solid waste sector are known as Smart Waste Technologies (SWT) and they contain elements of robotics, artificial intelligence, internet of things, cloud computing, data analysis and communication technology.
In developing countries – where access to public services is one of the main obstacles to improving the population’s well-being – technology can bridge provision gaps for safe, equitable and high-quality public services. One of the main challenges to proper solid waste management in Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC) is the production of efficient, reliable, and timely information on the entire solid waste chain by the entities that provide services and regulate management systems. Lack of information negatively impacts system follow-up, monitoring and control processes, as well as the design and implementation of public policies.
The following chart shows the potential uses and applications of digital technologies at every stage of the integrated solid waste management chain, including examples of how each of them contributes to the generation of data and system efficiency:
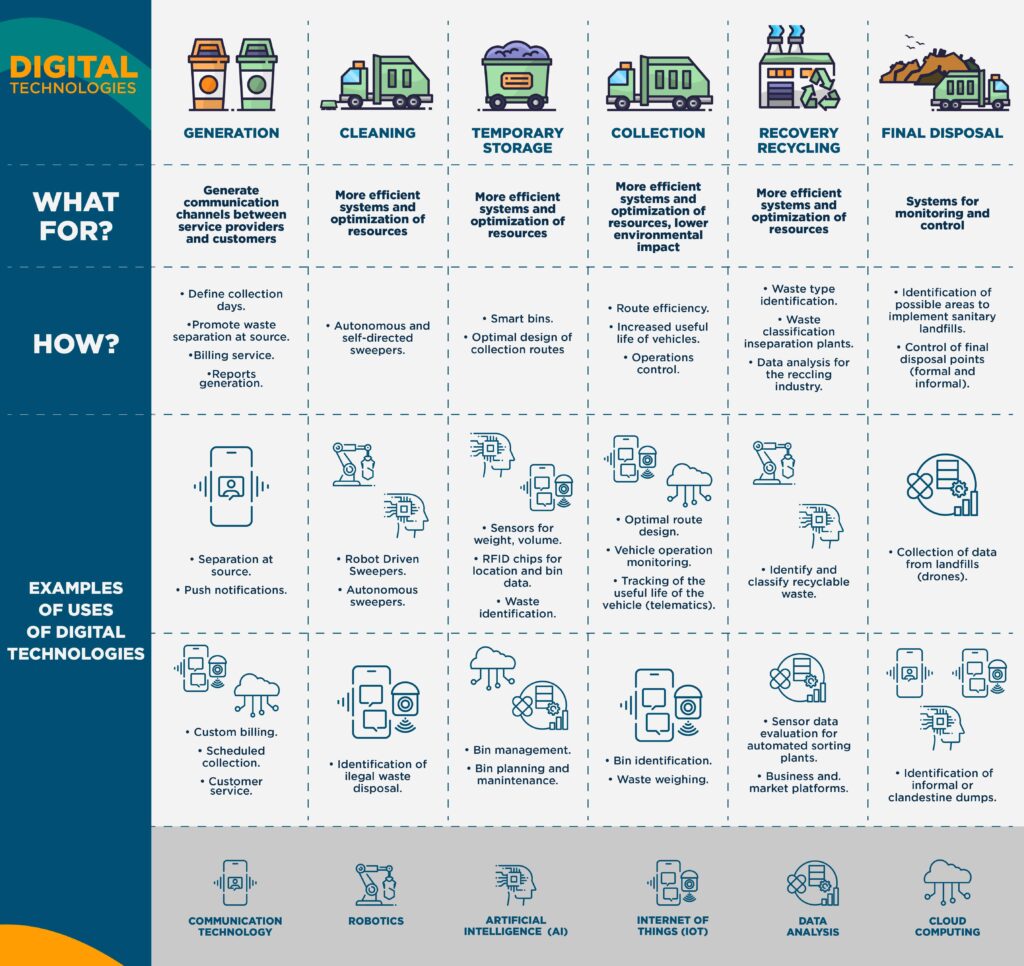
Chart 1. Use of digital technologies in the Integrated Solid Waste Management chain. (Author’s elaboration)
In this chain, collection logistics represents the stage with the most experience in digital technologies, and therefore, where most innovation has taken place. This has brought about a positive effect on contractors’ task planning, staff and machinery coordination, and data collection (ie, types of waste and quantity collected, follow-ups and monitoring operations, online incident reporting, vehicle life cycle, etc.)
The introduction and operation of smart bins can ensure efficient operations and optimize resources. Several companies have already deployed Internet of Things (IoT) technology, such as volume sensors or RFID chips to identify the exact location of bins. This enables efficient and secure information analysis, allowing service providers to make timely decisions. A pilot project in Santiago de Chile led the average collection frequency during the peak season to drop from 20 to 3.4 times per week.
Communication technologies, such as mobile apps for waste collection services, established communication channels between service providers and waste producers and produced data for personalized invoices. In many cases, these invoices contain QR codes or NFC tags, which provide information on the type and quantity of waste and its specific location for collection scheduling and delivery. Several apps have also been developed to identify litter in public spaces. For example, Pirika uses photos with GPS coordinates, data analysis and artificial intelligence to identify the type of waste located in a specific area and trigger cleanup interventions.
The future of solid waste management is digital, so we must understand existing digital technologies and their applications. Key players, particularly service providers and national and local governments, can gain important advantages by exploring digital innovation. This process must be accompanied by an understanding and an assessment of the technical, economic, and cultural capacities in each territory to ensure its efficiency and sustainability. Technology can be a key factor in narrowing the gaps for universal access to public services to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) faster and more efficiently.
4.0 technologies are revolutionizing all sectors. The IDB Group, through the Source of Innovation alliance, is mapping service providers that want to incorporate SWTs as well as start-ups currently working on digital technologies for solid waste management in the region to develop a contact network to meet future challenges in the sector.
Webinar: Smart Waste Technologies: The revolution in waste management

On March 2, the IDB held the Webinar Smart Waste Technologies: the revolution in waste management, last March 2, at 10:30 a.m. The main objective of this event was to promote the use of digital technologies to improve efficiency in municipal solid waste management systems and the potential use of these technologies in Latin America and the Caribbean, considering the characteristics of each territory, the main opportunities and challenges for their implementation, and the successful cases of technological innovation in service providers in the region.
Challenge: Implementation of Smart Waste Technologies

During the webinar we had the space to communicate about the Challenge: Implementation of Smart Waste Technologies (SWT), which aims to implement two (2) pilot projects to household solid waste with high potential for scalability that is presented jointly between service providers and startups / scaleups / digital SMEs.
The projects presented must have their own budget and investment capital for an effective implementation. The IDB Group, through Source of Innovation, will provide support to service provider entities interested in incorporating SWT and startups/scaleups/digital SMEs/companies that have SWT services, with the aim of designing and implementing pilot projects with scalability features in smart technologies. Additionally, Source of Innovation will provide 30k to each of the two selected projects for their strengthening and scaling.
If you are interested in participating, we invite you to fill out the form for service providers until March 15th of 2023.
Guest author
*Paula Guerra
Solid waste and inclusive recycling consultant for the IDB. Previously worked at the Ministry of Environment of Ecuador as manager of the National Solid Waste Management Program, and in the Municipality of Quito as Coordinator of Logistics and Recycling in the city’s sanitation company. She has worked as a consultant for different entities in Latin America. She has a Master’s degree in Sustainable Development from the University of London and advanced studies in Solid Waste Management with UNESCO IHE.

great, it is very important issue worldwide…
I love this. It is important to introduce IoT technology to wastes management in the world.